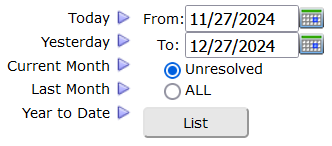
From the main menu, the menu choice Randoms, navigated to the module that lists random selections for all accounts and consortia for dates specified by the user. The page also included other report options the developers felt did not best serve the user from that page. Since the change, in order to navigate in a single click directly to the List Randoms module, you will find a new short cut icon under the menu:

The updated menu now navigates to a page that presents the List Randoms option as the first link on the page, and includes a variety of other reports to help users better manage random selections.
The first option on the page is where the Randoms menu previously navigated: List Randoms by Date. The other options on the new page provide data management reports so users can list accounts that need randoms conducted by a scheduled date. You will also find a link to a feature that send emails to accounts with a notification of upcoming randoms so they can update their participant list.
For many DTN subscribers, random selections are not conducted for every account, as a Stand Alone account or as a member of a consortium.
For an account to be included in reports related to random selection, the account must be a member of a consortium, or considered Stand Alone. To be a Stand Alone account for random selection report considerations, its Random Selection Participant attribute must be turned ON (set to Yes). You will find the attribute, Random Selection Participant, (Participates in Random Selections) in the account profile editor under the section: Random Selection Parameters.
Stand Alone Accounts & the Random Selection Participant Attribute:
An account that’s a member of a consortium is automatically considered a random selection participant.
If an account is not a member of a consortium, it’s considered a Stand Alone account, however, Stand Alone accounts are included in random selection summary reports, scheduled random selections, and mass emails regarding random selections, only if its Random Selection Participant attribute is set to Yes.
Use the report Report Accounts Not flagged as Random Participants (Non-Consortium Members to list all Stand Alone accounts (i.e., non-consortium members ) whose account attribute, Random Participant, has not been turned on. The report includes a link to open the account profile editor, or turn the attribute ON for multiple selected accounts.
Email Notification:
On the new page, you will find the email utility to send notifications that random selections will be conducted soon so the account can update their participant list. The email is sent to all consortia member accounts, and Stand Alone accounts whose account attribute, Random Participant, is set to Yes.
Scheduled Random Selections:
You can specify the date to generate the next random selection for every Stand Alone account, and although the platform does not automatically generate random selections on these scheduled dates, there are reports available on the new page to list accounts by their scheduled date so the TPA can easily manage randoms and helps ensure every account stays in compliance.
Accounts without a date specified for the next Random Selection:
You will find a report to list all accounts that do not have a specified date for their next random selection.
To generate random selections by date, the random selection profile for the account must include a date, Next Random, to indicate when the selection is anticipated. When the random is generated, the date will roll forward, based on the Frequency, however, a scheduled date must first be specified.
Note: Frequency is a random selection profile attribute and determines how the scheduled date is rolled forward when a random selction is generated. The date is rolled forward to be consistent, i.e., the order of the day-of-week, with the earlier date. If the earlier date is the third Thursday of the month, then the rolled forward date will also be the third Thursday of the month.
These are the current Frequency attributes you can choose:
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Bi-Annual
- Annual
This report will list all Stand Alone accounts that do not have a date yet specified. For an account to be considered Stand Alone, the account attribute, Participates in Randoms, must be turned ON. You’ll find this attribute under the section Random Selection Parameters in the Account Profile editor. Also note, this page provides a report that lists all accounts that do not have the Random Participant attribute turned ON.
Generating Random Selections by Schedule:
You can list Accounts by their date scheduled for the next random selection.
This option lists accounts with a scheduled date within a calendar period specified by the user. This feature is designed to help easily generate randoms so accounts are not overlooked. When you generate a random selection, the Next Date is rolled forward based on the Frequency attribute defined in the account’s random selection profile.
From the report you can easily generate a random selection for each account listed using the familiar random selection control. You can also select multiple accounts, with a check-box, and generate the random selection for all of them in a single request.
Note: The system does not automatically generate randoms – the user must initiate the randoms manually. The user can generate randoms for multiple accounts in a single request.
Random Selection Summary Reports:
You’ll find the four summary reports on the new page. In an effort to improve the List Randoms module, those reports were removed and added to the new page.
1. Summarize Randoms Conducted for ALL Accounts:
This report shows random selections for all accounts, including each account’s annual percentage targets and accumulated Year-to-Date (YTD) percentages (based on the average number of people over the number of randoms conducted) for both the substance and alcohol test.
2. Show ALL Random Participants with ZERO Randoms:
This report shows all accounts flagged as a Random Selection Participant (meaning it is an account for which you planned on generating a number of random selections for the year) for which no random selections have yet been generated.
3. Summarize Consortia Random Selections:
This report shows all the random random selections conducted for each consortium defined for your installation, including their annual percentage targets and their accumulated Year-to-Date (YTD) percentages (based on the average number of people over the number of randoms conducted) for both the substance and alcohol test.
NOTE: This report does not include random selections for accounts included in random selections for a consortium. Also, random selection test results that were created as the result of a consortium random selection are not included in the accumulative numbers for YTD percentages.
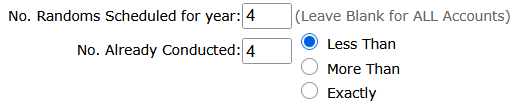
4. Less Than / More Than / Exactly: Summarize No. of Randoms Conducted:
For Stand Alone accounts you can use this summary report to list accounts that have not had enough selections yet generated.
For example, the numbers in the screenshot below will report all accounts that have been scheduled for 4 randoms (quarterly) but have had less than 4 random selections generated, to date.
![]() to get an overview how search works.
to get an overview how search works.![]() to read how to easily manage the search options.
to read how to easily manage the search options.![]() to open the Search Options Panel where you’ll find all the options fully presented similarly as in the earlier version of the feature.
to open the Search Options Panel where you’ll find all the options fully presented similarly as in the earlier version of the feature.![]() to cycle through search options without clutter.
to cycle through search options without clutter. that cycles through the options in that section when clicked.
that cycles through the options in that section when clicked. or the label Open Options Panel.
or the label Open Options Panel.